Intuition
In Starcraft, what order of buildings do you need to build so that you can build the Arbiter Tribunal?
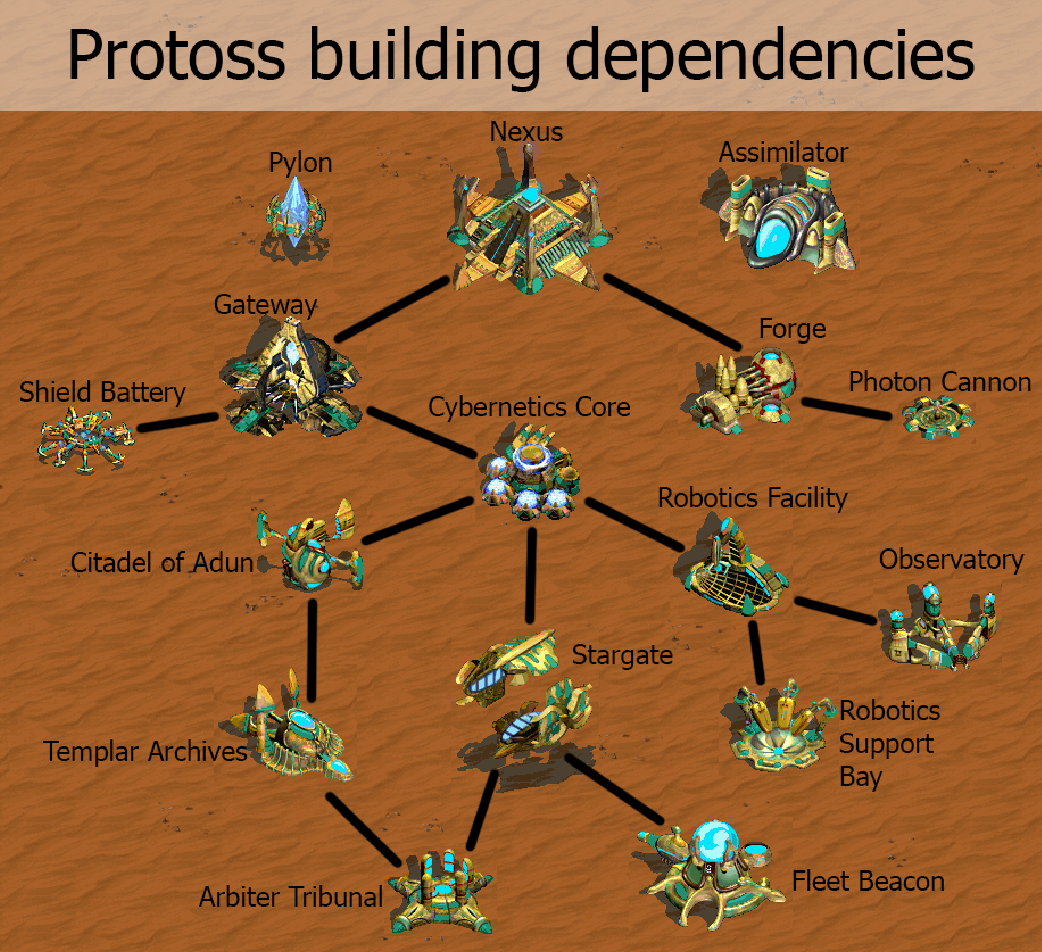
Answer: Nexus, Gateway, Cybernetics Core, Citadel of Adun, Stargate, Templar Archives, Arbiter Tribunal
Topological sort gives you this order. Kahn’s algorithm also figures out if there are cycles in the graph!
Algorithm
def kahn_topological_sort(graph):
# graph is a dictionary mapping each vertex to a list of its dependencies
# initialize in-degree dictionary
indegree = {vertex: 0 for vertex in graph}
# count the number of incoming edges for each vertex
for vertex in graph:
for dependency in graph[vertex]:
indegree[dependency] += 1
# add vertices with zero in-degree to the queue
queue = deque([v for v, count in indegree.items() if count == 0])
# process vertices from the queue
order = []
while queue:
# dequeue a vertex and add it to the order
current_vertex = queue.popleft()
order.append(current_vertex)
# reduce the in-degree of its dependencies by one
for dependency in graph[current_vertex]:
indegree[dependency] -= 1
# if the in-degree becomes zero, add it to the queue
if indegree[dependency] == 0:
queue.append(dependency)
# Optional: if there can be a cycle check it by comparing these lengths:
if len(order) < len(graph):
return None # CYCLE!
return order
🤔 indegree? wtf?
“indegree[vertex]” == “arrows pointing at vertex” == “how many vertices depend on vertex”
🧠 Remember!
graph[A] = [B, C, D] means “in order to build A, you need to first build B, C & D”.
Done 🎉🎉🎉
Appendix: Optional observations
- Note that, in the intuition example, order between Stargate & Citadel of Adun doesn’t matter. The algorithm gets one possible order. Typically, leetcodes clarify that order doesn’t matter in this case.
Appendix: Other tutorials online
Appendix: Related Leetcodes
Course Schedule: This problem asks you to determine if a given number of courses can be finished given a list of prerequisites. You can use topological sort to check if the graph of courses and prerequisites is acyclic and has a valid ordering.
Course Schedule II: This problem is similar to the previous one, but it also asks you to return the ordering of courses that allows you to finish all courses. You can use topological sort to find such an ordering or return an empty array if there is none.
Alien Dictionary: This problem asks you to find the lexicographical order of an alien language given a list of words from the dictionary. You can use topological sort to build a graph of characters and their dependencies and find the order that satisfies them.
Minimum Height Trees: This problem asks you to find the roots of minimum height trees for a given undirected graph with n nodes. You can use topological sort to remove the leaves of the graph iteratively until you have one or two nodes left as the roots.
Longest Increasing Path in a Matrix: This problem asks you to find the length of the longest increasing path in a given matrix. You can use topological sort to build a graph of cells and their dependencies based on their values and find the longest path in the graph.
Sequence Reconstruction: This problem asks you to check if a given sequence of integers can be reconstructed by concatenating the subarrays of another sequence. You can use topological sort to build a graph of integers and their dependencies based on the subarrays and check if the given sequence matches the order.
Find Eventual Safe States: This problem asks you to find all the nodes in a directed graph that are eventually safe, meaning that they cannot reach a cycle. You can use topological sort to reverse the edges of the graph and remove the nodes that have no incoming edges until you have only safe nodes left.
Sort Items by Groups Respecting Dependencies: This problem asks you to sort n items into m groups such that each group is sorted among themselves and respects the beforeItems dependencies. You can use topological sort to first sort the groups and then sort the items within each group.
Course Schedule IV: This problem asks you to answer queries about whether one course is a prerequisite of another course given a list of prerequisites for n courses. You can use topological sort to find the order of courses and then use dynamic programming or binary search to answer the queries efficiently.
Strange Printer II: This problem asks you to determine if it is possible to print a given target grid with different colors using a strange printer that can only print rectangles with one color at a time. You can use topological sort to build a graph of colors and their dependencies based on the grid and check if there is any cycle in the graph.